Jiao’s Scalp Acupuncture
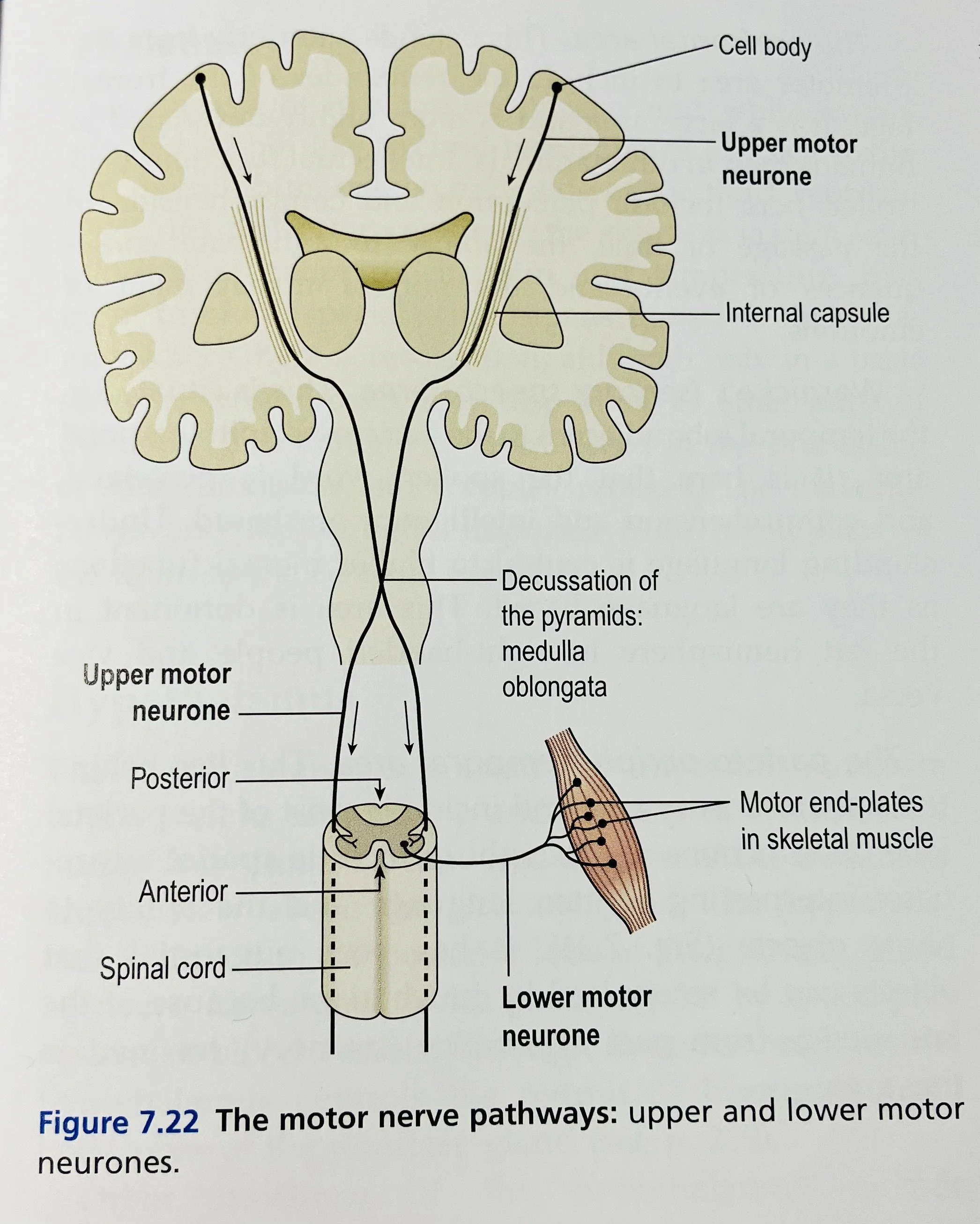
Jiao Shunfa, drawing on clinical experience and the principle of functional localization in the cerebral cortex, developed the system of Jiao’s Scalp Acupuncture. By mapping cortical functional areas—such as the motor, sensory, and language regions—onto the scalp surface, he defined specific therapeutic zones for needle stimulation. This approach has demonstrated significant clinical effectiveness in treating neurological conditions such as stroke, paralysis, and aphasia.
Brain Anatomy & Physiology
Chinese Scalp Acupuncture content is based on the Anatomy & Physiology of the brain
Jiao’s Scalp Acupuncture
Jiao Shunfa, drawing on clinical experience and the principle of functional localization in the cerebral cortex, developed the system of Jiao’s Scalp Acupuncture. By mapping cortical functional areas—such as the motor, sensory, and language regions—onto the scalp surface, he defined specific therapeutic zones for needle stimulation. This approach has demonstrated significant clinical effectiveness in treating neurological conditions such as stroke, paralysis, and aphasia.
T Point (Top of Motor Line / Scalp Point T)
The T point is located at the midpoint between the apices (tips) of both ears,
or alternatively, it can be defined as the midpoint between the glabella (the area between the eyebrows) and the external occipital protuberance (inion).
—————
Motor Area (Scalp Acupuncture) – Location and Indications
Upper point of the Motor Area: Located 0.5 cm posterior to the midpoint of the midline of the head (point T).
Lower point of the Motor Area: Located at the anterior border of the temporal hairline (temporal notch).
Indications by Motor Area Sections:
Upper 1/5 of the Motor Area:
➤Used to treat paralysis of the lower limb and trunk.Middle 2/5 of the Motor Area:
➤ Used to treat paralysis of the upper limb and trunk.Lower 2/5 of the Motor Area (also called Speech Area I):
➤ Used to treat facial paralysis, aphasia, drooling, and speech disorders.
—————
Sensory Area (Scalp Acupuncture) – Location and Indications
Location of the Sensory Area:
Upper point: Located 2 cm posterior to the T point (which is also 1.5 cm posterior to the upper point of the Motor Area).
Lower point: Located at the anterior border of the temporal hairline (temporal notch).
This line runs parallel and posterior to the Motor Area.
Indications by Section:
Upper 1/5 of the Sensory Area
➤ Treats:
Sensory disturbances of the lower limbs, trunk, and head
Numbness, paresthesia
Head and neck pain, dizziness, tinnitus
Middle 2/5 of the Sensory Area
➤ Treats:
Upper limb sensory dysfunction, such as:
Pain, numbness, paresthesia
Lower 2/5 of the Sensory Area (also called Speech Area I)
➤ Treats:
Facial numbness
Migraine
Temporomandibular joint disorders (TMJ)
_______
Dizziness and Auditory Area – Location and Indications
📍 Location:
Starts 1.5 cun above the ear apex (Erjian)
Extends horizontally 2 cm forward and 2 cm backward, forming a 4 cm horizontal line centered above the ear apex
📌 Indications:
Dizziness (vertigo)
Tinnitus
Hearing loss
___________
Vasomotor Area - Location and Indications
📍 Location:
Located 2.5 cm anterior to the T point
(or 3 cm anterior to the upper point of the Motor Area).
It runs parallel and anterior to the Motor Area, more forward than the Chorea and Tremor Control Area.
📌 Indications:
Primary hypertension
Cortical edema (cerebral or peripheral edema)
—————-
Chorea and Tremor Control Area – Location and Indications
Location:
This area starts 1 cm anterior to the T point
(or 1.5 cm anterior to the upper point of the Motor Area).
It runs parallel and anterior to the Motor Area.
Indications:
Chorea (e.g., Huntington’s disease)
Parkinsonian tremor
Parkinsonism syndromes
————-
Speech Area II – Location and Indications
📍 Location:
Located 2 cm inferior (downward) to the parietal tubercle
From that point, draw a 3 cm vertical line downward
📌 Indications:
Nominal aphasia (anomic aphasia) — difficulty in naming objects
Patients understand the function of an object but cannot recall its name
🧪 Clinical Example:
A patient sees a chair and knows it's for sitting, but cannot say "chair" — only says "sit"
_______
Speech Area III – Location and Indications
📍 Location:
Start from the midpoint of the Dizziness and Auditory Area (i.e., 1.5 cun above the ear apex)
Draw a 4 cm straight line posteriorly (toward the back of the head)
📌 Indications:
Sensory aphasia (Wernicke’s aphasia)
Patient has difficulty understanding spoken language
May respond inappropriately or speak fluently but meaninglessly
🧪 Clinical Example:
When asked “What is your name?”, the patient may reply with an unrelated answer
Appears fluent but cannot comprehend the question properly
——————
Practice Area (Apraxia Area) – Location and Indications
📍 Location:
Draw a line from the parietal tubercle (parietal eminence) to the mastoid process
Then draw two lines at a 40° angle in front of and behind this reference line
→ These angled lines represent the Practice Area boundaries
📌 Indications:
Apraxia (inability to carry out purposeful movements despite normal strength and coordination)
Disorders involving:
Muscle strength
Muscle tone
Basic motor execution
Motor planning and fine motor skills
___________
Lower Limb Motor-Sensory Area – Location and Indications
📍 Location:
Connect the upper points of the Motor Area and Sensory Area with a straight line
From this line, move 1 cm laterally (to the left and right sides)
From each lateral point, draw a line 3 cm in total length (1.5 cm forward, 1.5 cm backward)
The line runs parallel to the midline of the head
📌 Indications:
Paralysis, numbness, or pain in the contralateral lower limb
Acute lumbar sprain
Nocturia, urinary frequency
Uterine prolapse
_______
Visual Area – Location and Indications
📍 Location:
On the horizontal line at the level of the external occipital protuberance (枕外粗隆)
1 cm lateral to the midline (on both left and right sides)
From that point, draw a 4 cm straight line upward, parallel to the midline of the head
📌 Indications:
Cortical visual impairment
e.g. visual field loss or decreased vision due to occipital lobe dysfunction
Common in stroke, trauma, or cerebral ischemia
———————
Balance Area – Location and Indications
📍 Location:
Starting at the external occipital protuberance (粗隆水平線) level
3.5 cm lateral to the midline on both sides
From that point, draw a 4 cm straight line downward, parallel to the midline
📌 Indications:
Cerebellar diseases causing:
Ataxia (coordination disorder)
Balance problems
Dizziness (vertigo)
Brainstem dysfunction causing:
Limb numbness
Paralysis
___________
Stomach Area – Location and Indications
📍 Location:
Starting at the hairline directly above the pupil
Draw a 2 cm straight line upward, parallel to the anterior-posterior midline of the head
📌 Indications:
Gastritis
Gastric ulcer
Symptoms such as epigastric pain and upper abdominal discomfort
______
Thoracic Cavity Area – Location and Indications
📍 Location:
Medial to the Stomach Area, between it and the midline
At the level directly above the inner canthus (inner corner of the eye)
From the hairline, draw a 2 cm line upward and a 2 cm line downward, forming a 4 cm vertical line in total
The line is parallel to the anterior-posterior midline
📌 Indications:
Bronchial asthma
Chest discomfort
Respiratory-related disorders
————-
Genital Area – Location and Indications
📍 Location:
Start directly above the outer canthus (outer corner of the eye)
From the frontotemporal angle of the hairline (額角處), draw a 2 cm vertical line upward, parallel to the anterior-posterior midline
📌 Indications:
Disorders of the reproductive organs
Uterine bleeding
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Uterine prolapse